
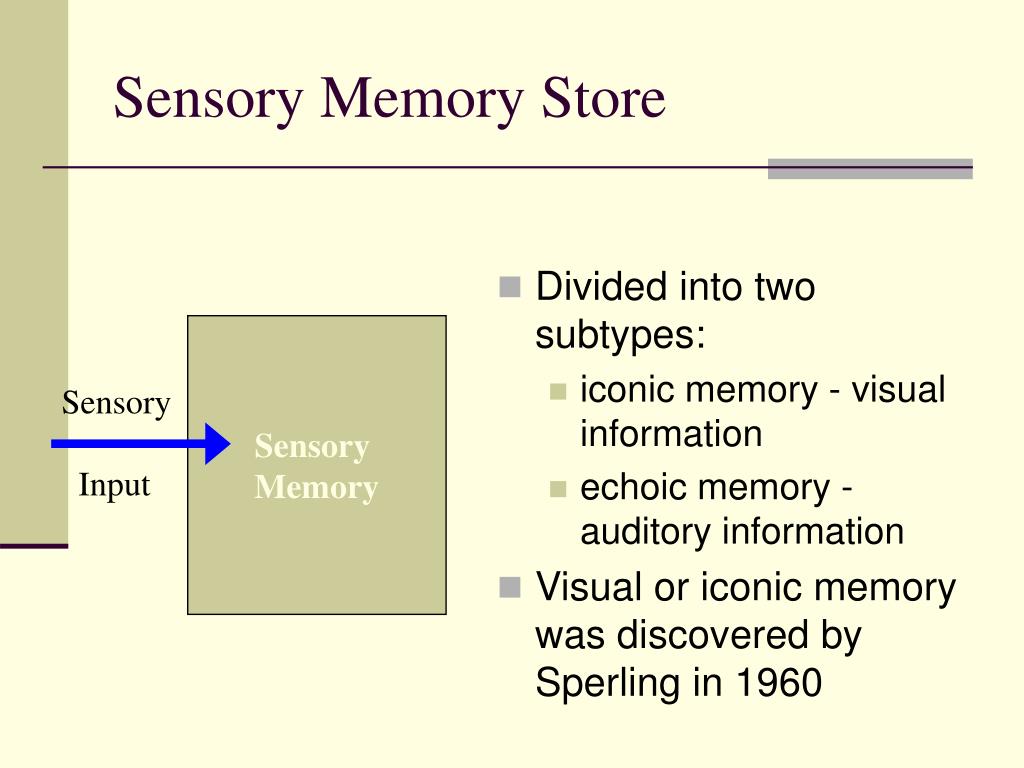
Sensory memory has a large capacity for information, but it has a brief duration. Sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory differ from each other, when it comes to the duration, capacity, and function. Olfactory memory (Input related to the sense of smell).Gustatory memory (Input related to the sense of taste).Iconic memory (Visual sensory input from the eyes).In the encoding process, a substantial amount of information is gathered through the sense of sight and hearing. It is believed that it includes systems that are associated with each sense. Our senses are working constantly, which is why we focus on a limited amount of information that we consider as relevant.
In the first stage of memory, an exact copy of the information gathered through the senses is stored for a very short duration.

The sensory memory associated with the sense of sight is referred to as the iconic memory, whereas the memory associated with the sense of hearing is referred to as the echoic memory. From the sensory information, only the inputs that you decide to pay attention to, move on to the short-term/working memory. In fact, the information is retained for the shortest duration in the sensory memory. The senses of sight and hearing hold on to the sensory input for a very brief duration. Before the information enters the short-term memory store, the data is acquired by our senses. The term ‘sensory memory’ refers to the first stage of memory that holds on to the incoming sensory/perceptual information. The model for human memory suggested by Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968) includes three components called sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. The human memory system involves the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information. For instance, while watching a motion picture, one doesn’t observe the gaps between frames, as each frame is held in the sensory register until the arrival of the next frame. Sensory memory, which is sometimes called a fleeting memory, gets consolidated as short-term memory, only if we choose to remember the event.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
