
Repetition – of elements in regular or cyclic fashion creates interest.The greater the contrast, the more something will stand out and call attention to itself. Contrast – is the juxtaposition of opposing elements (opposite colors, value light / dark, direction horizontal / vertical).can be used in creating balance in a composition. Objects, values, colors, textures, shapes,Įtc. Balance can be symmetrical, asymmetrical, or radial. A balanced work will have all the elements arranged such that the work will have a sense of visual equilibrium or stability.

Balance – is the distribution of interest or visual weight in a work.Some of the strategies employed to create degrees of importance are contrast of values, use of color, placement, variation, alignment, isolation, convergence, anomaly, proximity, size, and contrast. This is often used to train the viewer’s eyes on the center of interest, or a focal point – the area of interest the viewer’s eye naturally, instinctively skips to. Emphasis – is created by visually reinforcing something we want the viewer to pay attention to.How the principles of design are applied determines how successful one is in creating a work of art. If the elements are the ingredients, the principles are the recipe for a good work of art. These can be thought of as what we do to the elements of design.

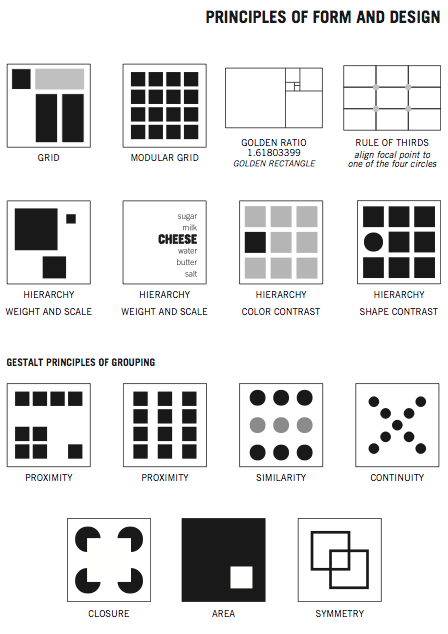
The next aspect to study are the principles of design. See the diagrams at the back of this article for examples and additional details.
Texture – is the surface quality of a shape, or how it appears to feel: rough, smooth, spiky, soft, hard, and glossy, etc. Value is also sometimes referred to as tone. Value – refers to how light or dark an object, area, or element is, independent of its color. Color is also sometimes referred to as hue. Color – is the visible spectrum of radiation reflected from an object. Space – is the distance or area around or between elements in a work. Size – refers to the relationship of the area occupied by one shape to that of another. Shape refers to a two-dimensional element with area on a plane, while form refers to a three-dimensional element Shape / Form – is a self-contained defined area, either geometric or organic. May be actual, implied, vertical, horizontal, diagonal, and/or contour. Line – is a continuous mark made on a surface or the edge created when two shapes meet. Some sources may differ on their exact list of elements and definitions, but this will get you started. Whether well done or not, all pieces of visual art will contain most, if not all, of these elements of design. These are the basic building blocks of any piece of art, and can be thought of as the ingredients used in your visual presentation. The first component to study is the seven elements of design. You’ve no doubt heard visual judges in the past make reference to the elements and principles of design, and if you’ve never really fully understood what they meant, this article is for you. If not, you’re probably only, at best, casually familiar with some of the basic tenants of good design.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
